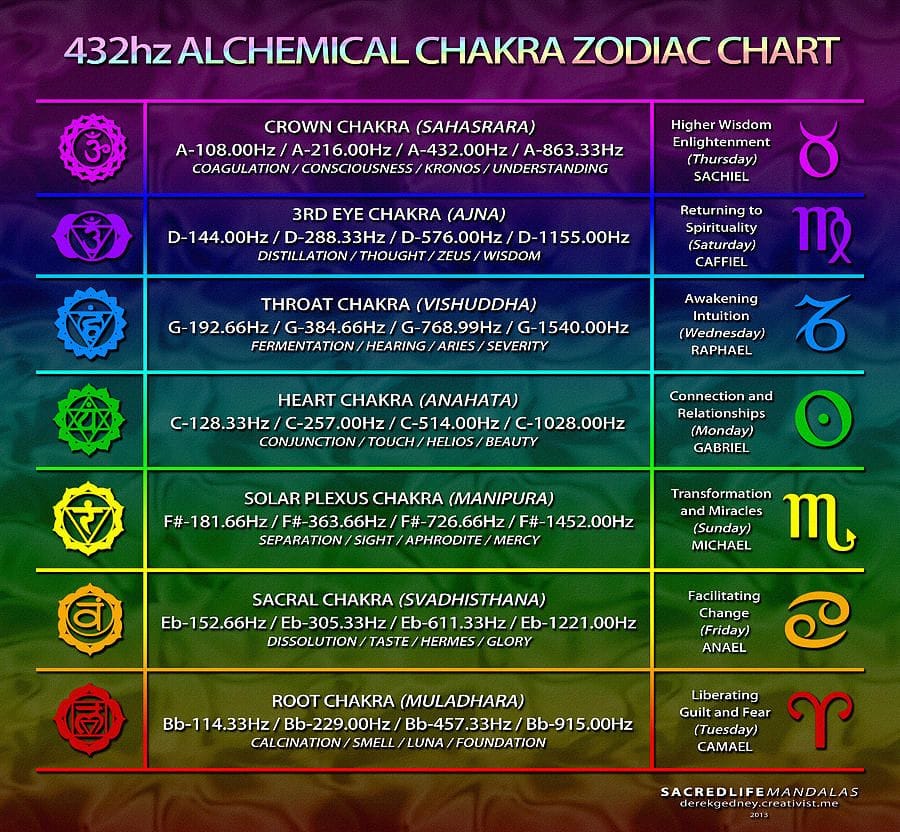
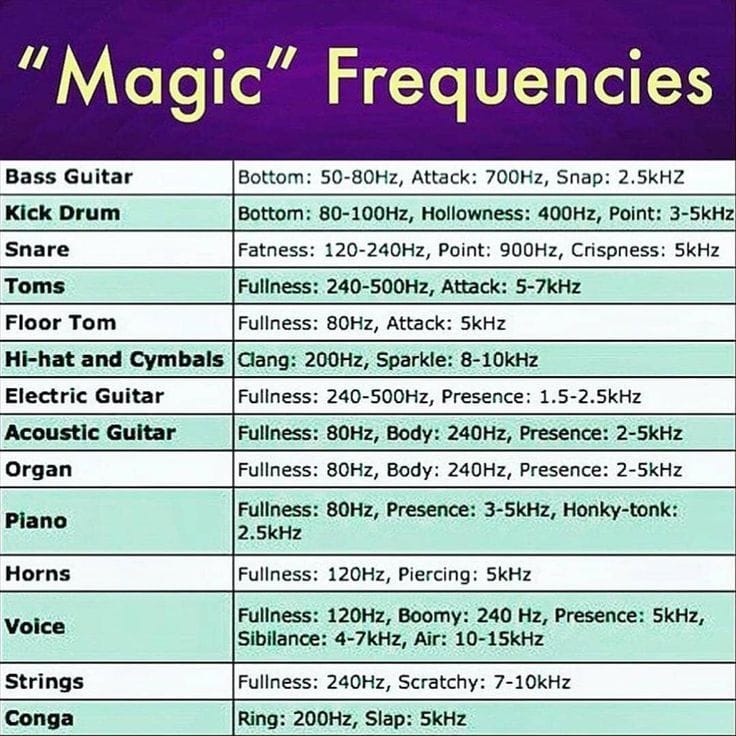
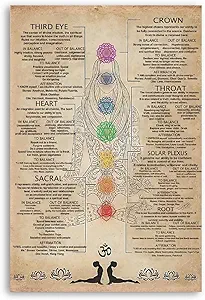
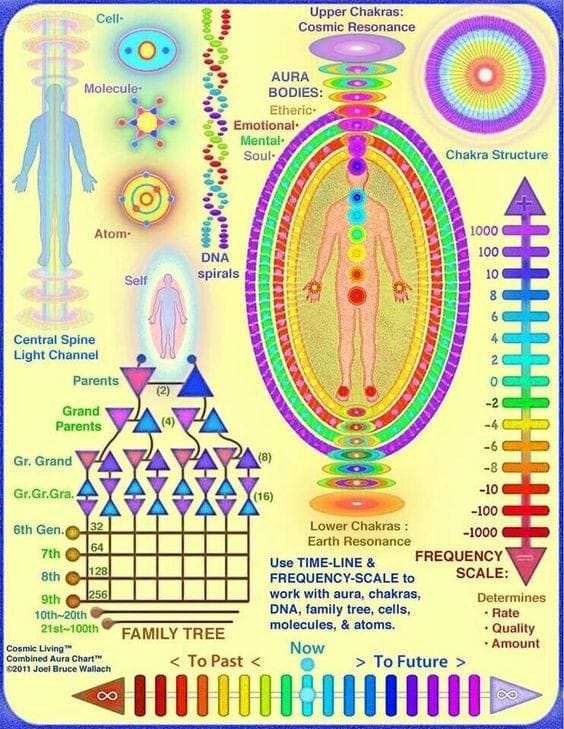
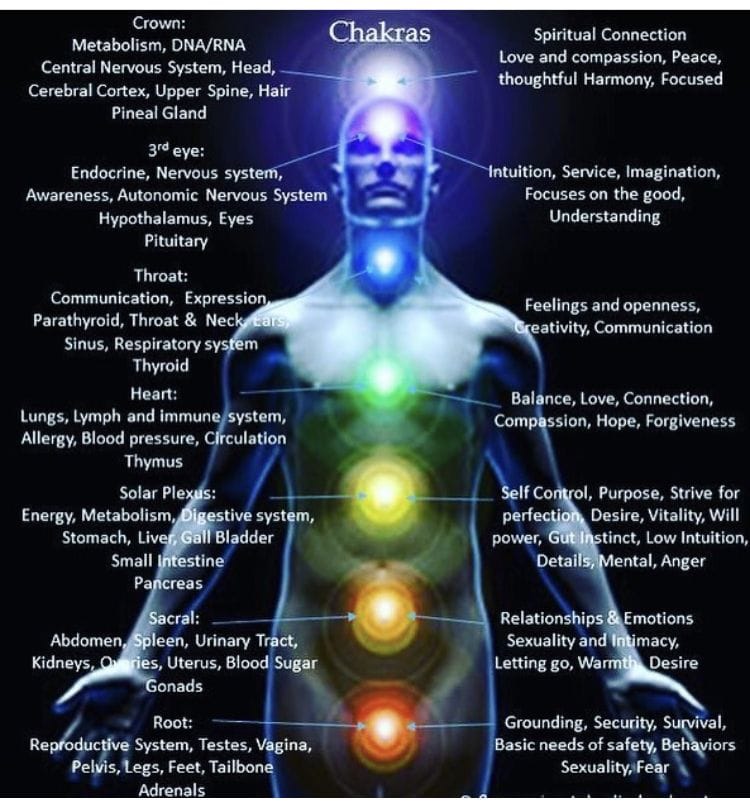
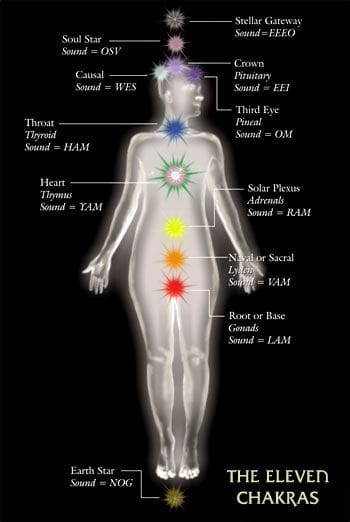
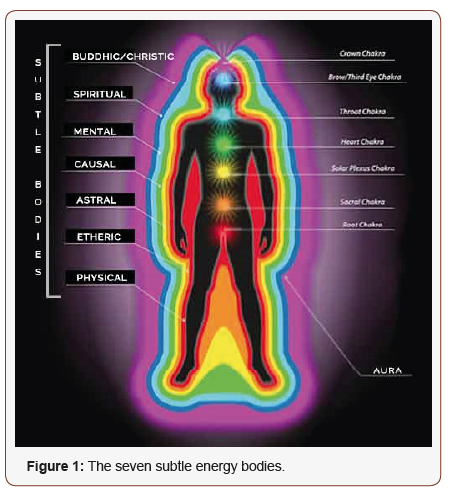
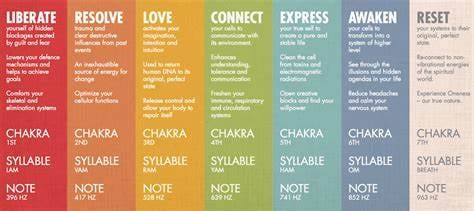
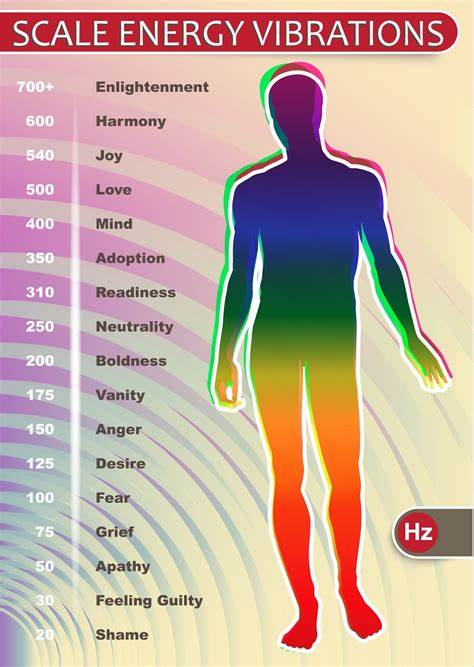
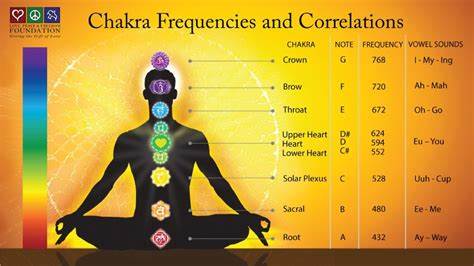
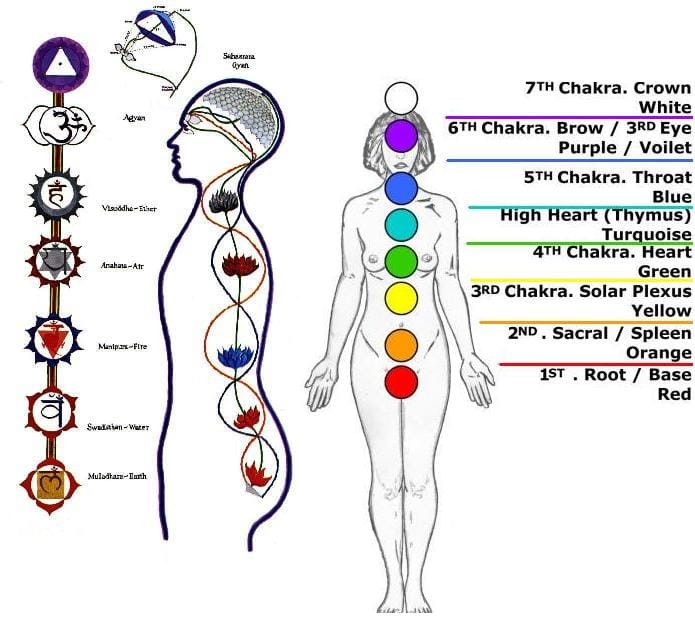
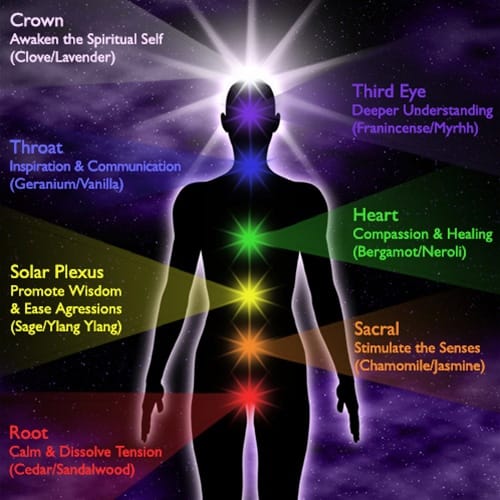
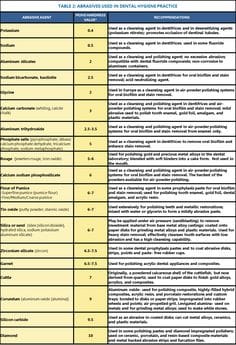
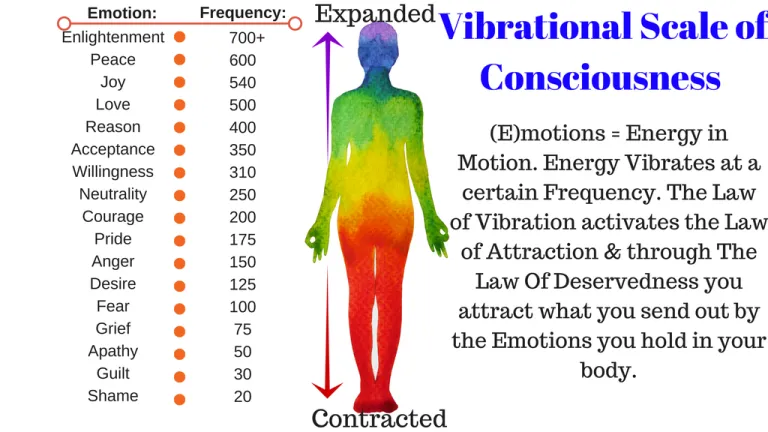
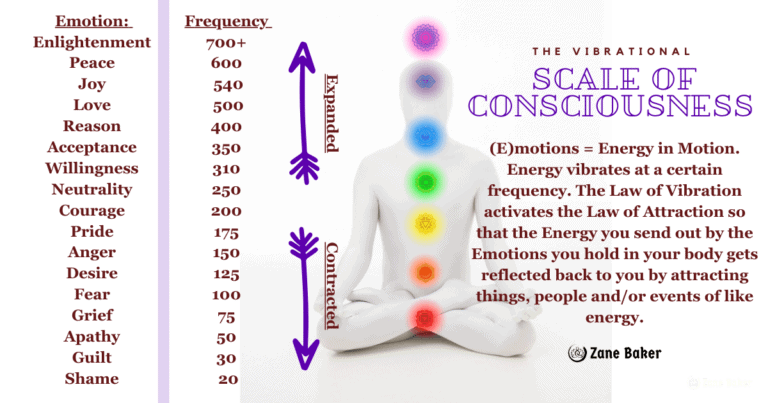
Frequency charts at bottom

Frequency effects




Middle frequencies, often referred to as midrange notes, play a crucial role in music and can have various impacts on the human body:
- Emotional Response: Midrange frequencies are where much of the emotional content of music resides. This is the frequency range where the human voice typically falls, allowing singers to convey emotion and connect with listeners on a deep level. As a result, midrange notes can evoke a wide range of emotions, from joy and excitement to sadness and nostalgia.
- Physiological Responses: Listening to music containing midrange frequencies can trigger physiological responses in the body. For example:
- Heart Rate: Certain midrange frequencies have been shown to influence heart rate. Upbeat music with prominent midrange notes can increase heart rate, while slower, more melodic music may have a calming effect.
- Respiration: Music with midrange frequencies can also affect respiration rate. Fast-paced music may lead to quicker, more shallow breathing, while slower, more soothing music can induce deeper, more regular breaths.
- Muscle Tension: Midrange frequencies can impact muscle tension and relaxation. Relaxing music with gentle midrange notes may help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation, while intense or dissonant midrange frequencies could increase tension in some individuals.
- Cognitive Effects: Midrange frequencies are essential for the intelligibility of speech and the perception of musical timbre. As such, they can influence cognitive processes such as:
- Attention: Music with clear midrange frequencies can capture and maintain the listener's attention. This is especially important in contexts where verbal communication or complex auditory information is involved.
- Memory: Midrange frequencies may enhance memory recall and cognitive processing. Melodies and lyrics containing midrange notes are often more memorable and easier to recall than those with extreme low or high frequencies.
- Physical Sensations: Midrange frequencies can produce physical sensations in the body, particularly when experienced at high volumes or through high-quality audio systems. These sensations may include:
- Tactile Vibrations: Vibrations from midrange frequencies can be felt as a physical sensation, especially in the chest and abdomen. This tactile feedback adds depth and richness to the listening experience, making the music feel more immersive.
- Warmth and Fullness: Well-balanced midrange frequencies contribute to the perceived warmth and fullness of sound. Music that lacks midrange frequencies may sound thin or lacking in depth, while music with an emphasis on midrange notes can sound rich and enveloping.
Overall, midrange frequencies play a critical role in shaping the emotional, physiological, and cognitive responses to music. By understanding how midrange notes affect the human body, musicians, composers, and audio engineers can create music that resonates deeply with listeners and elicits powerful emotional and physical experiences.
Certainly! Let's explore the impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body in more detail:
- Emotional Response:
- Expressive Communication: Midrange frequencies are where the human voice primarily resonates, allowing for clear articulation of speech and nuanced expression of emotions. When incorporated into music, midrange notes can convey a wide range of feelings, from tenderness and intimacy to passion and intensity. As a result, listeners often connect deeply with music that features prominent midrange frequencies, experiencing emotional responses that mirror the mood and sentiment expressed in the music.
- Physiological Responses:
- Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: The rhythmic patterns and emotional content conveyed through midrange frequencies can influence physiological responses such as heart rate and blood pressure. Upbeat music with energetic midrange notes may stimulate increased heart rate and circulation, while mellower melodies with soothing midrange tones can promote relaxation and reduce stress-related physiological responses.
- Respiration: Midrange frequencies can also affect breathing patterns. Music with midrange notes that are smooth and steady may encourage slow, deep breathing, fostering a sense of calmness and relaxation. In contrast, music with abrupt changes or dissonant midrange frequencies may elicit shallower, more irregular breathing patterns, reflecting heightened arousal or tension.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Attention and Focus: Midrange frequencies play a vital role in shaping the clarity and intelligibility of auditory information. Music with well-defined midrange notes tends to capture and maintain the listener's attention more effectively, facilitating focused engagement with the music and its message. This enhanced attentional focus can be particularly beneficial in contexts such as learning, productivity, and creative expression.
- Memory and Cognitive Processing: Midrange frequencies contribute to the distinctiveness and memorability of musical melodies and harmonies. Melodies containing prominent midrange notes are often easier to remember and reproduce than those with extreme low or high frequencies. Additionally, the emotional resonance conveyed through midrange frequencies can enhance cognitive processing and memory consolidation, leading to more profound and enduring musical experiences.
- Physical Sensations:
- Tactile Perception: Midrange frequencies can produce tactile sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body, particularly in the chest and abdomen. These tactile vibrations add a visceral dimension to the listening experience, creating a sense of immersion and physical presence. When experienced through high-quality audio systems or live performances, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can intensify the emotional and sensory impact of the music, heightening the listener's overall enjoyment and engagement.
By considering the multifaceted impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body, musicians, composers, and audio engineers can craft music that not only sounds aesthetically pleasing but also resonates deeply with listeners on an emotional, physiological, and cognition.

Certainly! Let's delve deeper into the impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body:
- Emotional Response:
- Empathy and Connection: Midrange frequencies are closely associated with the human voice, allowing for the clear transmission of emotions and intentions in speech and music. As a result, music containing prominent midrange notes often fosters a strong sense of empathy and connection between the listener and the performer. This emotional resonance can evoke feelings of comfort, understanding, and shared experience, enhancing the overall emotional impact of the music.
- Emotional Regulation: Midrange frequencies play a role in regulating emotional states by influencing the release of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain. Music with soothing midrange tones has been shown to reduce levels of stress hormones such as cortisol and promote the release of endorphins and oxytocin, which are associated with relaxation, pleasure, and social bonding. This can have profound effects on mood regulation and overall well-being, providing a natural and accessible means of emotional self-care and stress management.
- Physiological Responses:
- Autonomic Nervous System: Midrange frequencies can modulate the activity of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, respiration, and digestion. Music with calming midrange tones has been found to activate the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a relaxation response characterized by decreased heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension. Conversely, music with stimulating midrange frequencies can activate the sympathetic nervous system, increasing arousal and alertness.
- Immune Function: Emerging research suggests that exposure to music containing midrange frequencies may have beneficial effects on immune function. Preliminary studies have shown that listening to music with a balanced frequency spectrum, including midrange tones, can enhance immune markers such as natural killer cell activity and immunoglobulin levels. These findings suggest that music may have potential applications in supporting immune health and resilience.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Auditory Processing: Midrange frequencies are essential for auditory processing, speech perception, and language comprehension. Music with clear midrange notes facilitates the discrimination of speech sounds and the interpretation of verbal and nonverbal cues, improving communication and social interaction skills. This is particularly relevant for individuals with auditory processing disorders or communication difficulties, as well as for language learners and individuals in multicultural environments.
- Memory and Learning: Midrange frequencies play a role in memory formation and cognitive learning processes. Music containing familiar melodies and harmonies with distinct midrange tones is more likely to be remembered and recalled than music with ambiguous or unfamiliar frequency patterns. Additionally, the emotional resonance of midrange frequencies can enhance memory consolidation and retrieval, leading to deeper and more enduring learning experiences.
- Physical Sensations:
- Somatic Awareness: Midrange frequencies can evoke physical sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body, particularly in the chest, throat, and head regions. These somatic sensations add a tactile dimension to the listening experience, enhancing the sense of immersion and embodiment. When experienced through live performances or high-fidelity audio systems, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can intensify the listener's engagement and emotional response, creating a more profound and immersive musical experience.
In summary, midrange frequencies exert a wide range of effects on the human body, spanning emotional, physiological, cognitive, and somatic domains. By understanding and harnessing the therapeutic potential of midrange frequencies in music, we can promote health, well-being, and social connection across diverse populations and contexts.

Absolutely, let's further explore the nuanced impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body:
- Emotional Response:
- Empathy and Social Bonding: Midrange frequencies, being closely tied to the human voice, evoke strong emotional responses. When listening to music rich in midrange notes, individuals often experience heightened empathy and a sense of connection with the performer or composer. This emotional resonance fosters social bonding and can promote a sense of community among listeners, whether they are sharing a live performance or simply enjoying music together.
- Expressive Communication: Midrange frequencies enable the nuanced expression of emotions in both speech and music. Vocalists utilize midrange notes to convey subtleties of tone, timbre, and phrasing, allowing them to communicate complex emotional states effectively. Similarly, instrumentalists use midrange frequencies to imbue their performances with expressive qualities, enhancing the emotional impact and communicative power of their music.
- Physiological Responses:
- Stress Reduction and Relaxation: Music containing soothing midrange tones has been shown to induce relaxation and reduce physiological markers of stress. Listening to such music can lower heart rate, blood pressure, and cortisol levels, promoting a state of calmness and tranquility. This physiological relaxation response has important implications for stress management, sleep quality, and overall well-being.
- Pain Management: Midrange frequencies have analgesic effects and can modulate the perception of pain. Music therapy interventions incorporating midrange tones have been used to alleviate pain in various clinical settings, including hospitals, palliative care facilities, and rehabilitation centers. By engaging the body's natural pain-relief mechanisms and distracting attention from discomfort, music with midrange frequencies can provide effective pain management and enhance the patient's quality of life.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Memory Enhancement: Midrange frequencies play a crucial role in memory formation and retention. Music with clear, well-defined midrange notes is more memorable and easier to recall than music with muddled or indistinct frequency patterns. This mnemonic effect of midrange frequencies can be leveraged in educational settings to enhance learning outcomes and improve memory retention across diverse subject areas.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Music therapy interventions targeting midrange frequencies have shown promise in cognitive rehabilitation for individuals with neurological disorders such as dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and traumatic brain injury. By stimulating cognitive processes such as attention, memory, and executive function, music with midrange tones can help preserve cognitive function, enhance neural plasticity, and improve overall cognitive functioning in individuals with cognitive impairment.
- Physical Sensations:
- Tactile Stimulation: Midrange frequencies produce tactile sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body. These tactile stimuli add a tactile dimension to the listening experience, enhancing the sense of embodiment and physical presence. When experienced through live performances or high-fidelity audio systems, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can heighten the listener's sensory engagement and create a more immersive and visceral musical experience.
In summary, midrange frequencies exert a profound influence on the human body, eliciting emotional, physiological, cognitive, and somatic responses that contribute to the therapeutic and transformative power of music. By understanding and harnessing the unique properties of midrange frequencies, we can leverage music as a powerful tool for healing, well-being, and personal growth.

Certainly! Let's delve even deeper into the multifaceted impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body:
- Emotional Response:
- Empathy and Connection: Midrange frequencies are intimately linked to the human voice, allowing for the expression of emotions with clarity and nuance. When listeners hear music rich in midrange notes, they often experience a profound sense of connection with the performer or composer. This connection fosters empathy and emotional resonance, creating a shared emotional experience that transcends linguistic and cultural barriers.
- Mood Regulation: Midrange frequencies play a pivotal role in regulating mood and emotional states. Music containing soothing midrange tones can induce feelings of calmness, contentment, and introspection, while music with energetic midrange notes can evoke excitement, enthusiasm, and vitality. This mood-regulating effect of midrange frequencies has therapeutic implications for mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.
- Physiological Responses:
- Autonomic Nervous System Modulation: Midrange frequencies can modulate the activity of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, respiration, and digestion. Music with calming midrange tones has been shown to activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing physiological arousal. Conversely, music with stimulating midrange frequencies can activate the sympathetic nervous system, increasing alertness and arousal.
- Pain Management and Healing: Midrange frequencies have analgesic properties and can modulate the perception of pain. Music therapy interventions incorporating midrange tones have been used to manage pain in various clinical contexts, including during medical procedures, postoperative recovery, and chronic pain management. By engaging the body's endogenous pain modulation mechanisms, music with midrange frequencies can provide effective pain relief and enhance the healing process.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Attention and Concentration: Midrange frequencies play a crucial role in maintaining attention and focus during cognitive tasks. Music with clear midrange notes can enhance cognitive performance by reducing distractions and improving concentration. This attentional enhancement effect of midrange frequencies has practical applications in academic settings, workplace environments, and activities requiring sustained cognitive effort.
- Neuroplasticity and Brain Health: Midrange frequencies stimulate neural activity and promote neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize and adapt in response to experience. Music with midrange tones has been shown to enhance synaptic connectivity, neurogenesis, and neurotransmitter release, leading to improvements in cognitive function, memory consolidation, and learning capacity. These neuroprotective effects of midrange frequencies have implications for brain health and cognitive aging, offering potential strategies for preventing or mitigating age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Physical Sensations:
- Somatic Awareness and Embodiment: Midrange frequencies produce tactile sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body. These somatic sensations enhance the sense of embodiment and physical presence, creating a deeply immersive and visceral listening experience. When experienced through live performances or high-fidelity audio systems, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can heighten the listener's sensory engagement and evoke a profound sense of bodily resonance and interconnectedness.
In summary, midrange frequencies exert a wide range of effects on the human body, encompassing emotional, physiological, cognitive, and somatic dimensions. By understanding and harnessing the unique properties of midrange frequencies, we can leverage music as a potent therapeutic tool for promoting health, well-being, and holistic integration of mind, body, and spirit.

Absolutely, let's delve even further into the nuanced impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body:
- Emotional Response:
- Emotion Regulation: Midrange frequencies play a crucial role in regulating emotions by eliciting specific emotional responses in listeners. Music containing midrange notes can evoke a wide range of emotions, including happiness, sadness, nostalgia, and awe. These emotional responses are mediated by the brain's limbic system, which processes auditory stimuli and generates corresponding emotional states. As a result, music with well-crafted midrange frequencies can serve as a powerful tool for emotional self-regulation and mood modulation.
- Empathetic Resonance: Midrange frequencies, particularly those associated with the human voice, have a unique ability to evoke empathy and compassion in listeners. When individuals hear music rich in midrange tones, they often experience a sense of connection with the emotions expressed by the vocalist or instrumentalist. This empathetic resonance fosters interpersonal bonding and facilitates social cohesion, promoting a sense of shared humanity and interconnectedness.
- Physiological Responses:
- Stress Reduction: Midrange frequencies have been shown to have stress-reducing effects on the body, leading to decreased levels of cortisol (the stress hormone) and increased activation of the parasympathetic nervous system (responsible for relaxation). Music containing soothing midrange tones can induce a state of physiological relaxation, characterized by slower heart rate, reduced blood pressure, and relaxed muscle tension. This physiological response to midrange frequencies has significant implications for stress management, resilience-building, and overall health and well-being.
- Pain Management and Healing: Midrange frequencies can modulate the perception of pain and enhance the body's natural healing processes. Music therapy interventions incorporating midrange tones have been used to manage pain in various clinical settings, including hospitals, hospices, and rehabilitation centers. By activating the body's endogenous opioid system and releasing neurotransmitters such as endorphins and dopamine, music with midrange frequencies can provide effective pain relief and promote faster recovery from illness or injury.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Attention and Cognitive Performance: Midrange frequencies play a crucial role in maintaining attention and cognitive performance during various tasks. Music with clear midrange notes can enhance cognitive focus and concentration, leading to improved performance on cognitive tasks such as memory recall, problem-solving, and decision-making. This attentional enhancement effect of midrange frequencies has practical applications in educational settings, workplace environments, and activities requiring sustained cognitive effort.
- Neuroplasticity and Learning: Midrange frequencies stimulate neural activity and promote neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize and adapt in response to experience. Music with midrange tones has been shown to enhance synaptic connectivity, dendritic growth, and neurogenesis, leading to improvements in cognitive function, memory consolidation, and learning capacity. These neuroplastic effects of midrange frequencies have implications for cognitive rehabilitation, educational interventions, and strategies for optimizing brain health and cognitive performance across the lifespan.
- Physical Sensations:
- Tactile Perception and Embodied Experience: Midrange frequencies produce tactile sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body, particularly in the chest, throat, and head regions. These somatic sensations enhance the sense of embodiment and physical presence, creating a deeply immersive and visceral listening experience. When experienced through live performances or high-fidelity audio systems, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can heighten the listener's sensory engagement and evoke a profound sense of bodily resonance and interconnectedness.
In summary, midrange frequencies exert a wide range of effects on the human body, encompassing emotional, physiological, cognitive, and somatic dimensions. By understanding and harnessing the unique properties of midrange frequencies, we can leverage music as a potent therapeutic tool for promoting health, well-being, and holistic integration of mind, body, and spirit.

Certainly! Let's explore the intricate impacts of midrange frequencies on the human body in even greater detail:
- Emotional Response:
- Subtle Emotional Nuances: Midrange frequencies are uniquely adept at conveying subtle emotional nuances in music. They provide the foundation for melodic lines, harmonies, and vocal expression, allowing for the precise communication of a wide spectrum of emotions. From the tender resonance of a heartfelt ballad to the fiery intensity of a passionate aria, midrange frequencies imbue music with depth, richness, and emotional complexity.
- Emotional Resonance and Identity: Midrange frequencies resonate with the timbre of the human voice, which is closely linked to emotional expression and identity. When listeners hear music rich in midrange tones, they may experience a profound sense of resonance and familiarity, as if connecting with the essence of the performer or composer. This emotional resonance can evoke feelings of empathy, compassion, and shared humanity, fostering a sense of belonging and emotional connection within the listener.
- Physiological Responses:
- Balancing the Autonomic Nervous System: Midrange frequencies have the potential to balance the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, respiration, and digestion. Music containing soothing midrange tones can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing physiological arousal. Conversely, music with stimulating midrange frequencies can activate the sympathetic nervous system, increasing alertness and arousal. This dynamic interplay between sympathetic and parasympathetic activation contributes to the overall homeostasis of the body's physiological functions.
- Strengthening Immune Function: Midrange frequencies may also influence immune function by modulating immune markers and cytokine levels in the body. Preliminary research suggests that music containing balanced midrange tones can enhance immune activity and promote immune resilience. By stimulating the production of immune cells and enhancing immune surveillance, music with midrange frequencies may help bolster the body's defenses against infectious agents, pathogens, and other environmental stressors.
- Cognitive Effects:
- Enhancing Cognitive Flexibility: Midrange frequencies play a crucial role in enhancing cognitive flexibility and adaptive problem-solving. Music with clear midrange notes engages multiple cognitive processes simultaneously, including attention, memory, and executive function. This cognitive engagement fosters neural plasticity and cognitive resilience, enabling individuals to adapt to changing circumstances and navigate complex cognitive tasks more effectively.
- Facilitating Emotional Regulation: Midrange frequencies facilitate emotional regulation by modulating the activity of key brain regions involved in emotion processing, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Music containing soothing midrange tones can dampen amygdala activity and enhance prefrontal cortex function, leading to improved emotional regulation and stress management. This emotional regulation effect of midrange frequencies has important implications for mental health interventions and emotional well-being.
- Physical Sensations:
- Somatic Integration and Embodied Awareness: Midrange frequencies produce tactile sensations that are felt as vibrations within the body, particularly in the chest, abdomen, and throat. These somatic sensations enhance the sense of embodiment and physical presence, fostering a deeper connection between the listener and the music. When experienced through live performances or high-fidelity audio systems, the tactile feedback from midrange frequencies can evoke a profound sense of somatic integration and embodied awareness, grounding the listener in the present moment and enhancing the overall sensory experience.
In summary, midrange frequencies exert a multifaceted influence on the human body, encompassing emotional, physiological, cognitive, and somatic dimensions. By understanding and harnessing the unique properties of midrange frequencies, we can leverage music as a powerful tool for promoting health, well-being, and holistic integration of mind, body, and spirit.

what did egypt say
Egyptian civilization, particularly in ancient times, did not have a scientific understanding of frequency in the way we conceptualize it today. However, they did have a deep understanding of sound and its properties, especially in the context of their religious and cultural practices.
In ancient Egypt, sound played a significant role in religious rituals, ceremonies, and everyday life. They believed in the power of sound vibrations to influence the spiritual realm and communicate with gods and ancestors. For example, they used instruments such as drums, flutes, and rattles in religious ceremonies and processions to invoke deities and facilitate divine communication.
Additionally, Egyptians had advanced knowledge of acoustics, demonstrated by the construction of structures such as temples and tombs with specific acoustic properties. For instance, the design of the Great Pyramid of Giza is believed to have incorporated acoustical principles to enhance sound resonance and amplify vocalizations during rituals.
While ancient Egyptians may not have had a scientific understanding of frequency in terms of oscillations per second (Hertz), they certainly recognized the importance of sound vibrations in their cultural and religious practices. Their reverence for sound and its spiritual significance underscores the profound role that frequency, albeit in a different context, played in ancient Egyptian civilization.










![Guild of the Dragons -Knowledge Node [^]~~~~~Gratitude~~~~~[^] G0TD](https://guild-of-the-dragons.ghost.io/content/images/2024/02/depositphotos_1562554-stock-photo-golden-dragon.jpg)